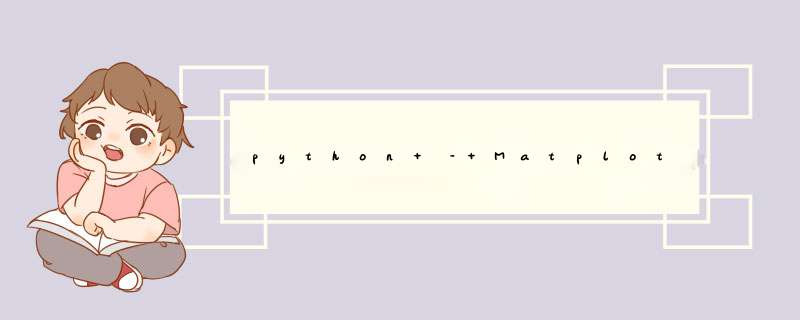
它适用于具有小半长轴(即“较小”轨道)的轨道.但是当我的轨道超越海王星(例如哈雷型彗星)时,从某些角度来看,有一种奇怪的“环绕式”(因为没有更好的词)效果.
让我告诉你我的意思:
图像编译:http://i.imgur.com/onSZG8s.png
>此图像从不会断裂的角度显示该图.
>当您向右旋转相同的绘图时,就好像轨道折成两半并反转方向!
>如果你从很远的距离观察情节,你可以看到椭圆被绘制成应有的.
这里是代码的最小版本,可以用来复制问题.只有当摄像机的视角与大轨道紧密平行时,才会出现“环绕”.
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3Dimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltdef orbitalElements2Cartesian(a,e,I,peri,node,E): """ Convert orbital elements to Cartesian coordinates in the Solar System. Args: a (float): semi-major axis (AU) e (float): eccentricity I (float): inclination (degrees) peri (float): longitude of perihelion (degrees) node (float): longitude of ascending node (degrees) E (float): eccentric anomaly (radians) """ # The source of equations used: # http://farsIDe.ph.utexas.edu/teaching/celestial/CelestialHTML/node34.HTML # Check if the orbit is parabolic or hyperbolic if e >=1: e = 0.99999999 # Convert degrees to radians I,node = map(np.radians,[I,node]) # True anomaly theta = 2*np.arctan(np.sqrt((1.0 + e)/(1.0 - e))*np.tan(E/2.0)) # distance from the Sun to the poin on orbit r = a*(1.0 - e*np.cos(E)) # Cartesian coordinates x = r*(np.cos(node)*np.cos(peri + theta) - np.sin(node)*np.sin(peri + theta)*np.cos(I)) y = r*(np.sin(node)*np.cos(peri + theta) + np.cos(node)*np.sin(peri + theta)*np.cos(I)) z = r*np.sin(peri + theta)*np.sin(I) return x,y,zif __name__ == '__main__': # Example orbital elements # a,incl,node orb_elements = np.array([ [2.363,0.515,4.0,205.0,346.1],[0.989,0.089,3.1,55.6,21.2],[0.898,0.460,1.3,77.1,331.2],[104.585332285,0.994914,89.3950,130.8767,282.4633] ]) # Setup the plot fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.gca(projection='3d') # Eccentric anomaly (full range) E = np.linspace(-np.pi,np.pi,100) # Plot the given orbits for i,orbit in enumerate(orb_elements): a,node = orbit # Take extra steps in E if the orbit is very large if a > 50: E = np.linspace(-np.pi,(a/20.0)*100) # Get the orbit in the cartesian space x,z = orbitalElements2Cartesian(a,E) # Plot orbits ax.plot(x,z,c='#32CD32') # Add limits (in AU) ax.set_xlim3d(-5,5) ax.set_ylim3d(-5,5) ax.set_zlim3d(-5,5) plt.tight_layout() plt.show()
我对此有点傻眼,似乎无法找到合适的解决方案.我非常感谢一些帮助!
解决方法 根据我的经验,matplotlib不适合复杂的3D绘图(我对轴外值有类似的奇怪行为).像mayavi这样的东西值得考虑,因为它是专为3D绘图设计的……在这个blog中给出了一个可能的解决方法,基本上只是将轴值设置为所需轴的np.NaN.如果我在您的示例中添加以下内容,
for r in [x,z]: for i in np.arange(len(r)): if r[i] < -5: x[i] = np.NaN y[i] = np.NaN z[i] = np.NaN elif r[i] > 5: x[i] = np.NaN y[i] = np.NaN z[i] = np.NaN else: pass
它消除了环绕.
总结以上是内存溢出为你收集整理的python – Matplotlib 3D绘图 – 从某些角度看参数曲线“环绕”全部内容,希望文章能够帮你解决python – Matplotlib 3D绘图 – 从某些角度看参数曲线“环绕”所遇到的程序开发问题。
如果觉得内存溢出网站内容还不错,欢迎将内存溢出网站推荐给程序员好友。
欢迎分享,转载请注明来源:内存溢出

 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫
 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫
评论列表(0条)